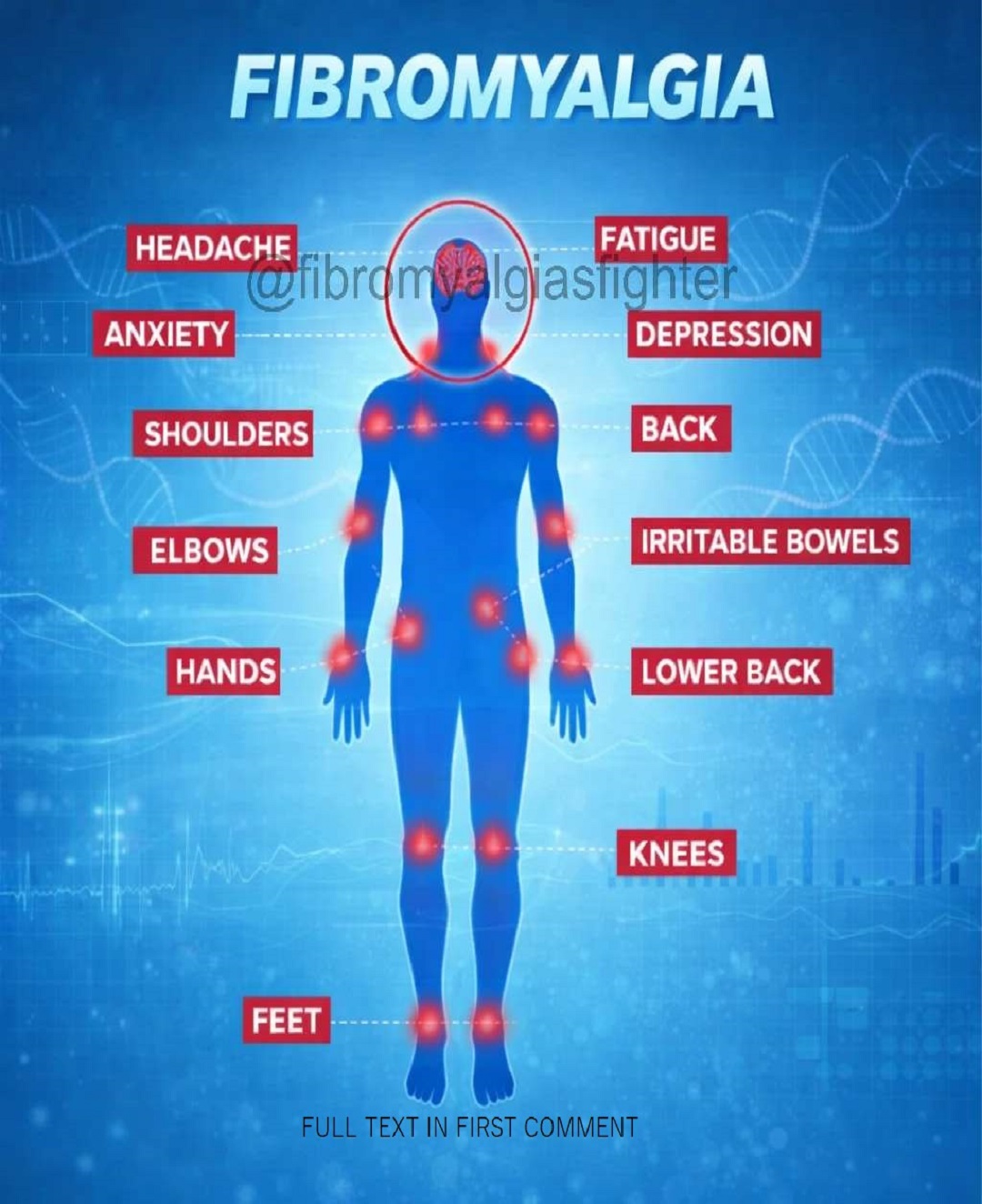
Fibromyalgia is a chronic neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Unlike typical pain caused by injuries or inflammation, fibromyalgia arises from changes in how the brain and central nervous system process pain signals. This systemic condition leads to widespread pain and a range of physical and emotional symptoms that significantly impact quality of life. Understanding these symptoms and their underlying causes is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers.
In this article, we will explore fibromyalgia in detail, including the most common symptoms, areas of the body affected, and the impact on daily life. We will also provide strategies for managing this complex condition, all while using relevant keywords to ensure SEO optimization.
What is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition of the central nervous system that causes widespread pain, fatigue, and a variety of sensory disturbances. It is considered a neurological disorder because it alters how the brain perceives pain and other stimuli. Unlike conditions such as arthritis or injuries, fibromyalgia does not cause visible tissue damage but instead leads to heightened sensitivity throughout the body.
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but research suggests a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. These changes in the central nervous system make individuals more sensitive to pain, even from stimuli that would not affect healthy individuals.
SEO keywords: fibromyalgia symptoms, chronic pain, central nervous system disorder, neurological pain, widespread pain
Common Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia manifests in both physical and emotional symptoms. The severity and combination of symptoms vary from person to person. Below, we explore the most common symptoms and how they affect different parts of the body.
1. Headaches and Migraines (Cephalgia)
Headaches, including tension headaches and migraines, are common in people with fibromyalgia. These are often linked to chronic muscle tension in the neck and shoulders, sleep disturbances, and heightened nervous system sensitivity.
Frequent headaches can interfere with concentration, work, and daily activities, making them one of the most challenging aspects of fibromyalgia for many patients.
Keywords: fibromyalgia headaches, tension headaches, migraine pain, chronic pain disorders
2. Persistent Fatigue
Fatigue associated with fibromyalgia is more than typical tiredness. It is a deep, persistent exhaustion that affects both physical and mental energy. Unlike normal fatigue, it does not improve with rest or sleep.
This fatigue is closely tied to poor restorative sleep, chronic pain, and overactivity of the nervous system. Patients often report feeling drained even after a full night’s rest, which can affect their ability to work, exercise, and maintain social relationships.
Keywords: fibromyalgia fatigue, chronic fatigue, sleep disorders fibromyalgia, tiredness in fibromyalgia
3. Anxiety and Nervousness
Anxiety is a frequent emotional symptom of fibromyalgia. Chronic pain and constant bodily stress can keep the nervous system in a heightened state of alert, making it difficult for patients to relax.
Symptoms may include excessive worry, tension, restlessness, and difficulty focusing. Anxiety can also worsen other symptoms, such as sleep disturbances and pain perception, creating a vicious cycle.
Keywords: fibromyalgia anxiety, chronic pain anxiety, nervous system hypersensitivity, fibromyalgia emotional symptoms
4. Depression and Mood Changes
Living with chronic pain, physical limitations, and social misunderstanding often contributes to depression in fibromyalgia patients. Changes in neurotransmitters linked to the condition may further affect mood regulation.
Patients may experience persistent sadness, feelings of discouragement, and loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities. Addressing both physical and emotional aspects of fibromyalgia is essential for comprehensive management.
Keywords: fibromyalgia depression, mood disorders, chronic illness mental health, fibromyalgia emotional impact
5. Shoulder Pain
Shoulders are commonly affected due to constant muscle tension. Pain can be deep, heavy, or burning, limiting the ability to lift arms, carry objects, or maintain posture for extended periods.
Muscle stiffness and soreness in the shoulders can worsen with repetitive movements or stress, making daily tasks like dressing or lifting groceries difficult.
Keywords: fibromyalgia shoulder pain, muscle tension, chronic musculoskeletal pain
6. Back and Spine Discomfort
Back pain is a hallmark of fibromyalgia, often affecting the entire spine. This pain results from core sensitivity, muscle stiffness, and poor sleep rather than structural damage.
Even without abnormalities in imaging tests, patients may experience severe discomfort, making standing, walking, or sitting for long periods challenging.
Keywords: fibromyalgia back pain, spine pain, chronic musculoskeletal disorders
7. Elbow Sensitivity
Elbows are particularly sensitive areas in fibromyalgia. Patients often report pain triggered by touch or pressure, even in the absence of inflammation or injury.
This heightened sensitivity is due to changes in the central nervous system rather than local tissue problems, making everyday tasks like typing or lifting objects painful.
Keywords: fibromyalgia elbow pain, nervous system hypersensitivity, tender points
8. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Many fibromyalgia patients also experience irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhea.
This overlap occurs because the nervous system regulates both pain perception and intestinal function, leading to gastrointestinal disturbances in addition to musculoskeletal symptoms.
Keywords: fibromyalgia IBS, gastrointestinal symptoms fibromyalgia, abdominal pain, chronic illness digestive issues
9. Hand Pain and Stiffness
Fibromyalgia can affect the hands, causing pain, stiffness, tingling, numbness, and swelling without visible changes.
These symptoms make fine motor tasks like writing, typing, or holding objects more difficult, affecting productivity and quality of life.
Keywords: fibromyalgia hand pain, stiffness, tingling sensations, chronic pain hand symptoms
10. Lower Back (Lumbar Region) Pain
The lumbar region often bears the brunt of fibromyalgia pain. Pain can be constant or come in waves, accompanied by stiffness and movement limitations.
This discomfort arises from muscular tension and nervous system sensitivity, rather than structural problems, emphasizing the systemic nature of fibromyalgia.
Keywords: fibromyalgia lower back pain, lumbar pain, chronic pain management
11. Knee Pain
Knee pain in fibromyalgia may occur even without joint damage. Patients report deep, heavy pain or sensitivity to touch, making activities like walking, climbing stairs, or standing for extended periods difficult.
This symptom highlights the importance of understanding fibromyalgia as a systemic, not localized, condition.
Keywords: fibromyalgia knee pain, joint sensitivity, chronic musculoskeletal pain
12. Foot Pain and Discomfort
Pain in the feet can manifest as burning sensations, fatigue, or sensitivity to footwear. In some cases, even light contact with the floor can cause discomfort.
Foot pain further limits mobility and affects daily activities, making proper management crucial for maintaining independence and quality of life.
Keywords: fibromyalgia foot pain, burning sensations, mobility issues, chronic pain
The Systemic Impact of Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is not confined to a single body part. Its effects are systemic, affecting the nervous system, muscles, joints, and even mood and cognition. Patients may experience:
-
Chronic widespread pain
-
Fatigue and poor restorative sleep
-
Emotional disturbances such as anxiety and depression
-
Sensory hypersensitivity
-
Gastrointestinal issues
Because symptoms can overlap with other conditions, fibromyalgia is often misunderstood, and patients may face challenges in receiving accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: systemic fibromyalgia symptoms, fibromyalgia pain management, chronic illness awareness
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Diagnosing fibromyalgia is challenging because symptoms are subjective and there are no specific laboratory tests for confirmation. Doctors typically rely on:
-
Patient history
-
Physical examination of tender points
-
Exclusion of other conditions with similar symptoms
Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing a comprehensive treatment plan, including medication, lifestyle adjustments, and alternative therapies.
Keywords: fibromyalgia diagnosis, tender points, fibromyalgia evaluation, chronic pain assessment
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for fibromyalgia, various treatments can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life:
1. Medication
Common medications include pain relievers, antidepressants, and anti-seizure drugs that help modulate pain signals.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
-
Regular low-impact exercise (yoga, swimming, walking)
-
Balanced diet to reduce inflammation
-
Sleep hygiene practices to improve restorative sleep
3. Stress Reduction
Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can alleviate anxiety and emotional stress.
4. Physical Therapy
Targeted therapies can reduce muscle tension, improve mobility, and relieve joint pain.
Keywords: fibromyalgia treatment, chronic pain management, fibromyalgia lifestyle, physical therapy fibromyalgia
Living with Fibromyalgia
Daily life with fibromyalgia requires adaptation. Patients may need to:
-
Pace activities to conserve energy
-
Use supportive devices for joints and mobility
-
Communicate with employers and family about limitations
-
Seek support from fibromyalgia communities
While challenging, proper management and self-care can significantly improve functionality and overall well-being.
Keywords: living with fibromyalgia, chronic pain coping strategies, fibromyalgia support
Conclusion
Fibromyalgia is a complex, chronic condition that impacts multiple areas of the body and mind. Its systemic nature makes it distinct from localized pain disorders, and symptoms range from widespread musculoskeletal pain to fatigue, emotional disturbances, and sensory sensitivity.
Understanding fibromyalgia’s symptoms, triggers, and management strategies is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers. While challenging, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with fibromyalgia can maintain functionality and improve their quality of life.